Introducion of Soil
The Uppermost Layer of the Earth which is Made up of a Mixture of Organic remains, Soil and RockS Material is defined as Soil. Soil is a very golden boon of life given by Nature because all the Food items, Plants and trees of Nature grow from Soil. It is also considered one of the Natural resources of God. Soil supports the life and growth of Plants. The Physical properties of Soil include Color, texture, structure, porosity, density, consistency, aggregate Stability, and temperature. These Properties influence processes such as Infiltration, Erosion, Nutrient Cycling and Boilogical activity.

Table of Contents
ToggleDo you know How Plants Make thier food in Soil
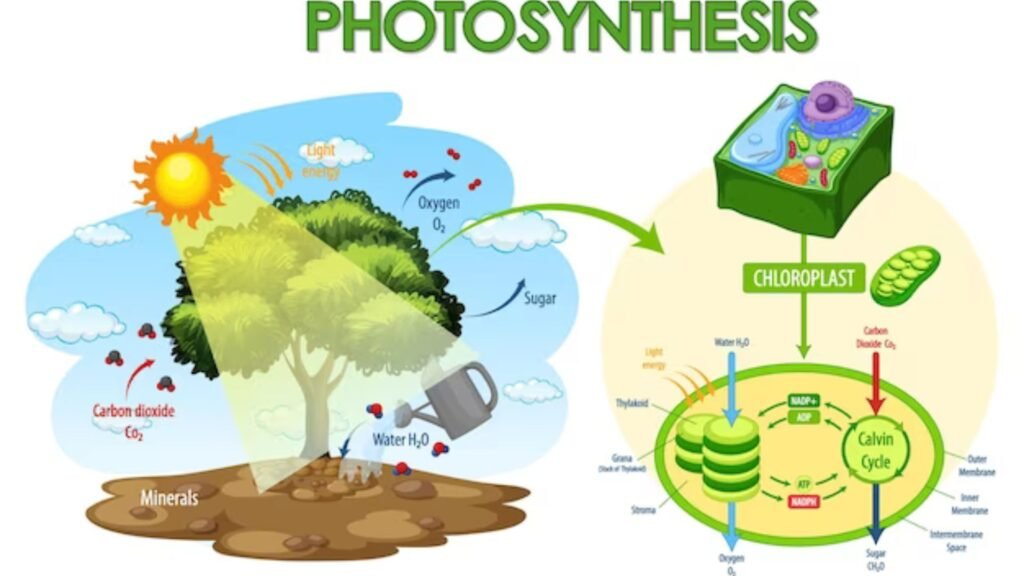
Plants make their own food is the process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. It is the primary way in which plants create their own food and release oxygen into the atmosphere
Physical Proprerties of Soil
These are Physical Properties of Soil

Physical properties of Soil include are :-
- Soil Colour
- Soil Texture
- Soil Structure
- Soil Porosity
- Soil Density
- Soil Stablity
- Soil Temperature
What is a Soil Colour

The Colors of the Soil is Mainly Form of 3 Main Colors: Black – from Organic Matter, Red – from iron and Aluminum Oxides, White from Silicates and salts. Depending on the indicators and factors of the soil condition, mainly organic matter and iron. on the amount and state of oxides as well as the amount of air and water in the Soil pores; In general, darker soils have higher organic matter content, brown soils are Waterlogged or anaerobic, brown soils are good
What is a Soil Texture

Soil texture refers to the hardness or fineness of the mineral particles present in the soil, while soil structure describes the physical arrangement of these particles. Texture and structure are important properties of soil that help determine the ability of the soil to supply water and nutrients to plants. For example, light soil refers to soil with more sand than clay, while heavy soil is composed largely of clay.
What is a Soil Structure

Soil structure is characterized by the combination and arrangement of primary soil particles, which form secondary structural units. From: Soil Health and Agroecosystem Intensification 2017.
What is a Soil Porosity

Soil porosity refers to the amount of pores or open spaces between soil particles. Pores are formed in the soil due to the movement of roots, insects and worms. Expansion of gases trapped in these places by groundwater and or disintegration of the original soil material. Soil texture also affects soil porosity.
What is Soil Density

Soil density is calculated from the mass and volume of a dry soil sample. Soil density is determined based on Uhland sampler in which the cylinder is inserted into the medium depth of the soil layer by the plant roots. Once the cylinder is removed, the sample is prepared, and taken to an oven to dry for 24 hours.
What is Soil Stablity

Soil stability is the ability of land to limit the redistribution and loss of soil resources by wind and water.
What is a Soil Temperature

Soil temperature represents a measure of the underlying heat of the ground. It controls soil chemistry and biology and atmospheric ground gas exchange. You also encounter the term soil surface temperature, which is a measure of the warmth and coolness in the top 4 inches (10 cm) of the ground.
What do you mean by Soil Conversion

Soil conservation is a combination of practices used to protect soil from erosion. First and foremost, soil conservation involves treating soil as a living ecosystem. This means returning organic matter to the soil on an ongoing basis.
Keyline design
Contour ploughing
Windbreakers
Terrace farming
Salinity management
Perimeter runoff control
Soil-conservation farming
Cover crops/crop rotation
Use of Green Manures
Stream Bank Protections
What is the Advantages of Soil

Soil provides plants with a base for their roots and holds the nutrients needed for plant growth. Soil filters rainwater and controls the drainage of excess rainwater, thereby preventing floods. It also protects against pollutants, thereby protecting the quality of groundwater.
See also
Disclaimer
The information provided on the topic “Properties of Soil || Types || Conversion || Structure || Easily Explanation” is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Thanks For Visiting. Have a Good Day
Visit my Website
Web Stories
प्रकृति में शुद्ध पानी के कितने स्रोत है हमें पिने के लिए शुद्ध पानी कहा से मिलता है आइये जानते है
By sciencestudy.fun
क्या आप जानते है की प्रकृति में मिट्ठी का क्या महत्व होता है मिटटी की संरचना कैसी होती है कैसे पेड़ और पौधे मिटटी से अपना खाना बनाते है आइये जानते है
By sciencestudy.fun
क्या आप जानते है बारिश के बाद ही आकाश में इन्द्रधनुष कैसे बनता है क्या विज्ञानं है इसके पीछे
By sciencestudy.fun





